Getting Started: WiNDC 2.0 Data Stream
Introduction
The input data for the
WiNDC 2.0 build stream are collected from various government
websites, they are parsed, cleaned and harmonized, similar data are joined, all data are
scrubbed to remove unnecessary information and finally they are transformed to
a format that can be read by GAMS. The output of this process is the GDX file
windc_base.gdx. It is included in the WiNDC build stream package,
windc_build.zip (163 MB).
This document describes how to construct the GDX file windc_base.gdx
from the original sources that are available from government agencies.
The files that facilitate data processing are written in Python 3.6. Python code relies on Python packages, so you first need to create the proper Python environment where all necessary packages are installed. See the instructions for details.
Downloads
-
All files for parsing and processing the data are available at
GitHub.
Click on the button "Clone or Download" to clone the repository to your local machine
or simply download a
.zipfile (80 KB) with all files.
Take care to not disrupt the directory structure. All data parsing should be performed in the directorywindc_datastream. - All raw data sources files: datasources.zip (153.6 MB).
- An SQL database with all data sources, readily parsed and joined: SQL (198.1 MB).
The WiNDC 2.0 Datastream
In this section we describe the data stream that creates the windc_base.gdx
data input file, so that users can construct this file themselves should they wish to do so.
The modular design of the data stream enables a wide audience to engage deeply with the data
and simplifies debugging processes. For more information, see Adam Christensen's
presentation.
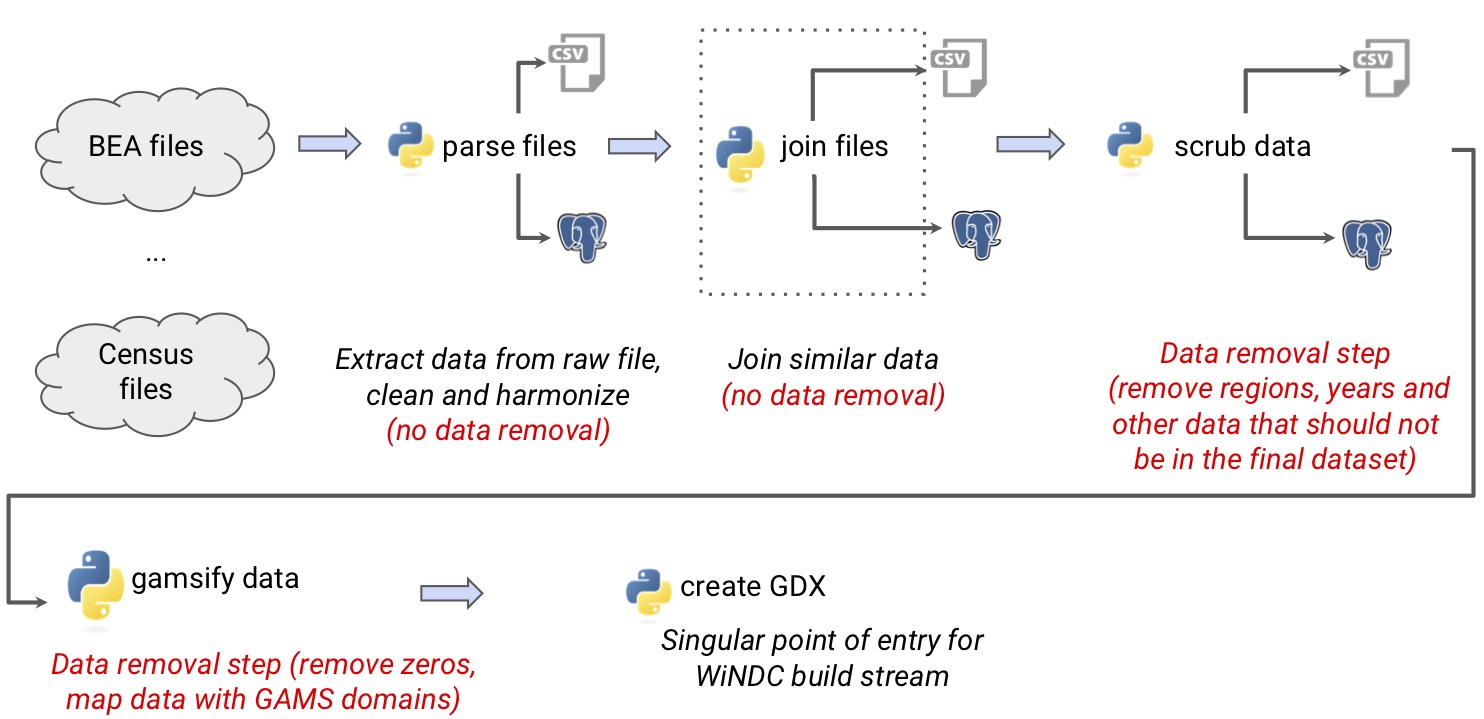
The raw data files that are available from various government agencies have different types (CSV, EXCEL), shapes and structures. These data structures must be unified and made ready for input into a GAMS model. The process of converting the raw data to the the GAMS readable GDX format requires three steps: data parsing, data scrubbing and data transforming.
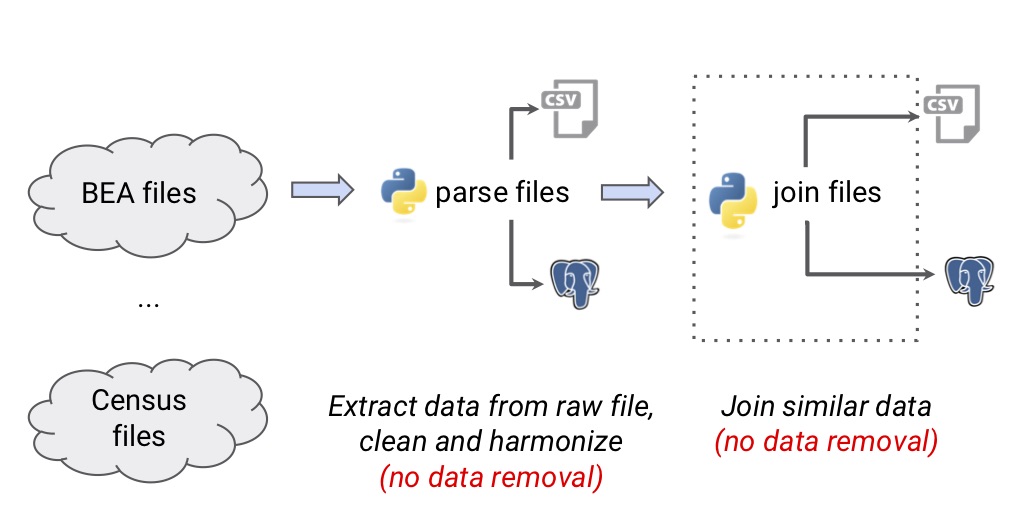
Data Parsing
In this step the data are extracted from raw data files, cleaned, harmonized and in some cases similar data are joined in one file. The following image illustrates this step:
Raw data are collected from the following government websites:
The raw data files from all these government agencies are available for
download
(datasources.zip, 153.6 MB).
Download the compressed file datasources.zip to the main directory,
windc_datastream-master. Unzip and thus create the directory
datasources. All parsing scripts will pull data from this directory.
The raw files are pased with the script
parse_XXX.py.
You can output the parsed data as a formatted CSV file or direct it
to a SQL database. Directions are given below.
A data harmonization step is part of the parsing process.
For example, it is important that all values that are in "US Dollars" and "USD"
have the same format. We chose "us dollars".
This harmonization and labeling step is controlled by the files in the
directory core_maps. Please do not
modify these files, as they are used in the build stream.
Unintended inconsistencies can result in spurious results or domain checking errors.
We provide these files to help you map the naming conventions to a more human readable format.
The files in the directory core_maps/gams
control how the raw data is converted to a consistent GAMS-friendly format.
Please do not modify these files to avoid uninteded conflicts.
If necessary, raw data that exists across several files is concatenated
with the script join_XXX.py.
Creating a CSV file
If you wish to transform the 71 Industry BEA Supply Input-Output tables
from their native EXCEL format into a .csv
file, use the following command:
python3 parse_bea_supply_io.py --csv-out
Follow this pattern to convert other data source files to a
.csv format.
We provide the file all_parse.py
for users who want to parse all data in one step. In this case, run the following
command:
python3 all_parse.py --csv-out
Loading the data into an SQL database
We assume that you are using a PostgreSQL database as the storage container. PostgreSQL is an open-source, production grade flavor of SQL. Installation details for PostgreSQL can be found here. First you need to create an empty database. Then you can direct data to this database where a new table will be created for the respective dataset. The following command creates a table with the data from the 71 Industry BEA Supply Input-Output tables in your SQL database:
python3 parse_bea_supply_io.py
If you wish to parse all data in one step and load them to your SQL database, run the following command:
python3 all_parse.py
All details of the SQL connection engine can be found in the
file sql_engines.py. If you wish to use a different flavor
of SQL, you need to modify this file. However, note that
the flavor of SQL has to be compatible with the Pandas
method .to_sql. For more information, see the
Pandas documentation.
Data Scrubbing
In this step the data are scrubbed to remove unnecessary information that
should not exist in the final dataset. The scripts scrub_XXX.py perform
this task. The following image illustrates this step:
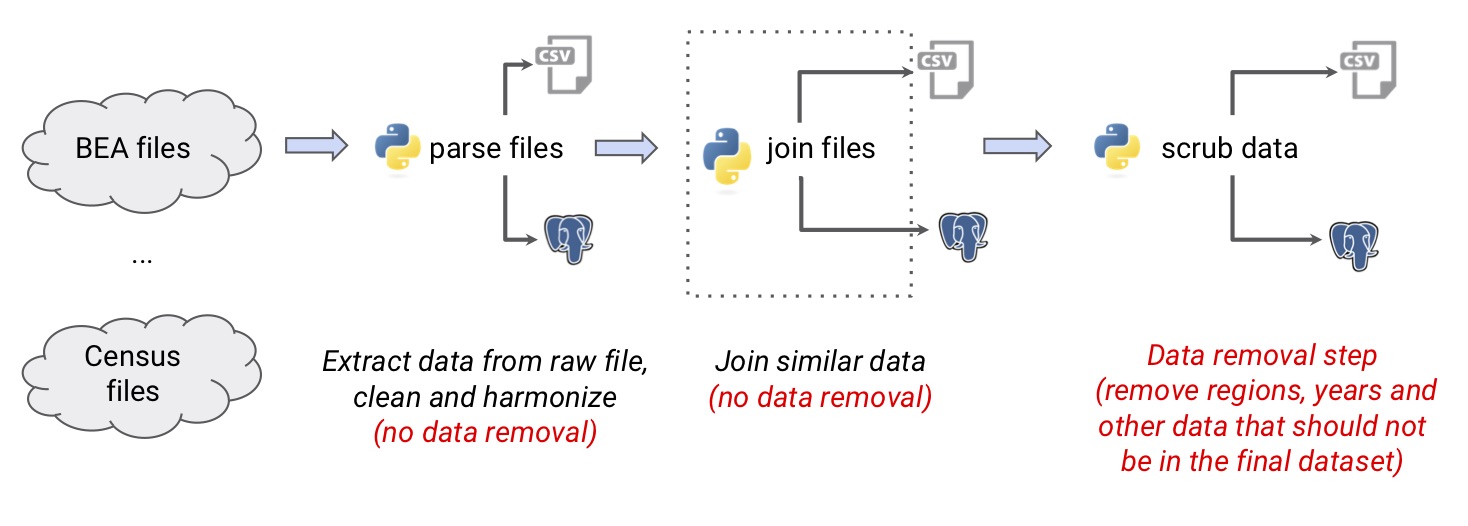
The scrubbing operations may be started in two ways:
-
from the raw data files in the directory
datasources, - from input data that are already parsed and compiled in an SQL database made available from WiNDC.
If you wish to start from the SQL database provided by WiNDC, please follow these steps:
-
Install PostgreSQL by following
these instructions. PostgreSQL is an open-source, production grade flavor of SQL.
If you wish to use a different flavor of SQL, you need to modify the file
sql_engines.py. However, note that your chosen flavor of SQL has to be compatible with the Pandas method.to_sql. For more information, see the Pandas documentation. -
Download the file
windc_sql.gz (198.1 MB) and move it to the directory
windc_datastream-master. -
Execute the following command in the directory
windc_datastream-master:Heregunzip -c windc_sql.gz | psql dbname
dbnameis the local name of the created database. Note that this name should be consistent with the name in the filesql_engines.py. The command above is a piped operation between thegunziputility andpsqland is appropriate for larger databases. Your local SQL database is now ready to be used.
If you wish to interrogate the scrubbed State Energy Data System (EIA-SEDS) dataset starting at the SQL database, execute the following command:
python3 scrub_seds.py --csv-out
Alternatively, if you wish to create a CSV copy of the data from the original
data flow in the datasources directory, execute:
python3 scrub_seds.py --csv-out --no-sql
Note that simply executing python3 scrub_seds.py will not output anything.
This pattern of command line boolean flags is the same for all scrub_XXX.py files.
Note that you can generate all scrubbed CSV files in one step with the following command:
python3 all_scrub.py --csv-out [--no-sql]
Here the flag is --no-sql is optional and depends on your choice of source
for the input data.
Data Transforming
In this step the data are transformed to prepare them for the downstream WiNDC processes.
Zeros are removed and data are mapped to GAMS domains.
The ouput is the GDX database windc_base.gdx that serves as input for the
WiNDC build stream.
If you wish to create the file windc_base.gdx from scratch
from the SQL data origin, execute the following command:
python3 all_gamsify.py
To create the GDX file from the raw data files, run:
python3 all_gamsify.py --no-sql
Note that the file windc_base.gdx must be moved to the directory
windc_build/build_files for the WiNDC build stream.
The image below illustrates the whole data stream process: